The Difference Between Horse Wormers. Not all wormers are the same. Do you know which is the best choice for your horse? Different wormers target different worms and parasites.
An easy and inexpensive way to find out if your horse is infested is to get a sample of your horses manure. Your Vet will run a fecal egg count exam to know which, if any wormer is needed. If the fecal egg count exam comes back negative, there is no need for worming at that particular time.
Keep in mind tapeworms do not show up in a horse’s manure. Two choices are a blood test or a test such as the EquiSal Tapeworm Test. A swab of saliva is taken from the horse and sent off to be analyzed. These tests will rule out or confirm if your horse has tapewormsD
What worms/parasites can affect a horse?
The four most common types of internal parasites are Ascarids, Bots, Strongyles and Tapeworms.
Ascarids (roundworms)
The larvae of this worm start its growth in the small intestine and then migrate through the liver, the lungs and finally, the pharynx or throat where it gets swallowed again. The worm returns to the small intestine to mature and reproduce. Roundworms can be an issue with younger horses up to about 15 months of age

because of their lack of immunization against the worms. A heavy infection can cause weight loss, stunt the young horse’s growth, give a rough hair coat and/or pot-bellied appearance, and cause lethargy and/or colic.
Bots
Adult flies lay yellow-colored eggs to the horse’s forelegs, chest and shoulders. As the horse grooms itself, the horse’s saliva releases the egg adhesive and the larvae then enter the mouth. Once ingested, the larvae travel and attach to the lining of the stomach where it causes irritation, digestive issues and obstruction. After 8-10 months, the larvae are passed in the feces and then burrow into the ground to pupate. They surface from the ground as adult flies and repeat the cycle.
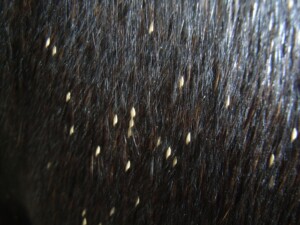
Strongyles (blood or red worms)
Found as three different species – S. vulgaris (up to 25mm), S. edentatus (up to 40mm) and S. equinus (up to 50mm). Strongyle infection occurs by ingestion of the larvae, which begin their transformation into parasites as they travel down the animal’s intestine. The S. vulgaris can cause damage in the cranial mesenteric artery, eventually causing colic, gangrenous enteritis, or intestinal stasis and possibly rupture. The other two species are active blood feeders that can lead to anemia, weakness, emaciation and diarrhea.

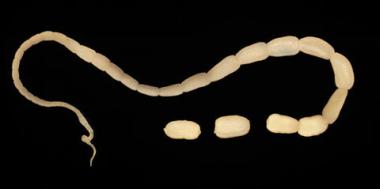
Tapeworms
Tapeworms take a different approach to infecting your horse. Forage mites in the grass eat tapeworm eggs. The tapeworm larvae then develop within the mites. The horse ingests the forage mites during grazing. Now that the larvae are in the horse’s gut they can develop into maturity. They adhere themselves to the gut wall at the ileo-caecal junction, thusly increases the risk of intestinal obstruction or rupture due to inflammation at the attached site.
How does a horse get worms/parasites?
Horses can get worms when turned out with infected horses or when they are turned out in a contaminated pasture. In both cases, it is likely the horse will become infected. Pastures become contaminated with the eggs and larvae or parasitic worms through the manure of an infected horse’s manure. This then mixes in the grass of the pasture. As your horse grazes, the eggs and larvae are ingested. A pasture can stay infected for a considerable amount of time so always keep that in mind.
How do I know if my horse has worms/parasites?
By appearance, your horse can appear to be in good health but it still can be infected with worms. Common signs of worm/parasite infection include:
- Colic
- Diarrhea
- Dull coat
- Lethargy
- Lack of appetite
- Loss of condition
- Loss of weight
- Visual evidence of worm around horse’s rectum
Again, the best method for confirming whether or not your horse has worms is to have your vet perform a fecal egg count and/or blood test. These tests confirm the species of parasite, provide an idea of how many adult worms are in the intestine, and give an estimate on how badly your pasture is infested. The blood test measures chemicals in the blood produced by inflammatory responses to the migration of the larvae.
What can I do to help prevent my horse from getting worms?
Manage pastures –
- Remove and dispose of manure in the pasture. This will aid in reducing the population of eggs and larvae. Mowing and harrowing the pasture exposes the larvae to predators and the elements and helps to decrease the population.
- Rotate horses in different pastures, rest the pasture for six months if possible.
- Keep the number of horses per acre to a minimum.
- Don’t feed off the ground.
- Routinely run fecal egg counts – This will definitively tell you which (if any) parasites your horse is dealing with as well as determine the effectiveness of your worming program.
- Worm your horse as needed – Worming your horse with the proper wormer helps remove adult worms from the intestine and reduces the chance of re-infection by decreasing the number of ineffective larvae in the feces and, in turn, the pasture.
The Difference Between Horse Wormers
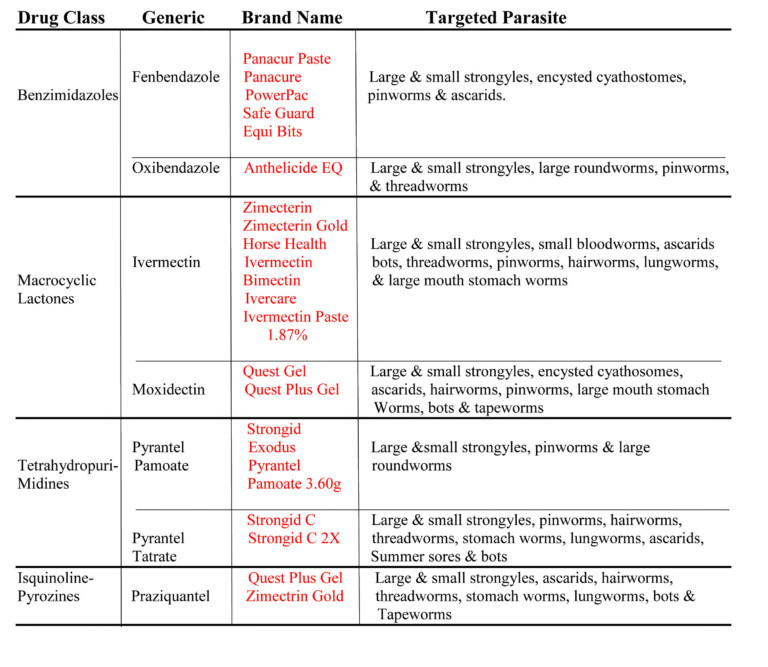
How often should I worm my horse?
“Back in the day” owners wormed their horses every 8 weeks whether they needed it or not! It was also suggested to switch up wormers for maximum effectiveness. Again, if you have a fecal egg count and/or bloodwork done you remove the guess work as to IF your horse needs to be wormed AND which wormer to use.
Some things to consider:
- Age of horse.
- A fecal egg count test performed by your vet.
- Has your horse been exposed to other horses with worms/parasites OR been in a new pasture?
- Choose the wormer necessary to kill the worms that were detected in the fecal egg count test.
- Only worm when necessary.
- Follow dosage directions.
As always, invest good bacteria into your horse’s gut with any worming protocol, vaccinations, antibiotic therapy, steroid therapy, etc… If possible for one week prior, during and one week following any of the above, by adding Equine Challenge Probiotic or Equine Challenge Probiotic Blast your horses diet.
Refer to your veterinarian for an effective wormer schedule.
Kathy Hartwig

